Introduction to Metrology Applications in IC Manufacturing
Author(s): Bo Su; Eric Solecky; Alok Vaid

Book Description
Metrology has grown significantly, especially in semiconductor manufacturing, and such growth necessitates increased expertise. Until now, this field has never had a book written from the perspective of an engineer in a modern IC manufacturing and development environment. The topics in this Tutorial Text range from metrology at its most basic level to future predictions and challenges, including measurement methods, industrial applications, fundamentals of traditional measurement system characterization and calibration, semiconductor-specific applications, optical metrology measurement techniques, charged particle measurement techniques, x-ray and in situ metrology, hybrid metrology, and mask making. The accompanying CD includes example spreadsheets of measurement uncertainty analysis—specifically, precision, matching, and relative accuracy.
Book Details Date Published: 25 September 2015 Table of Contents SHOW TABLE OF CONTENTS | HIDE TABLE OF CONTENTS Preface 1 Introduction 1.1 What is Metrology? 1.2 Measurements and Metrology 1.3 Metrology in Daily Life 1.4 Applications in Modern Manufacturing 1.5 Standards and Traceability 1.6 Metrology Standards Related to IC Manufacturing 1.7 Measurement Methods and Process 1.7.1 Operator, measurement system, and measurement target 1.7.2 Manual measurement versus automatic measurement 1.8 Applications of Industrial Metrology References 2 Metrology Fundamentals: Measurement System Characterization and Calibration Using Traditional Definitions 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Precision 2.3 Long-Term Stability 2.4 Accuracy 2.5 Linearity 2.6 Tool-to-Tool Matching: Multiple Measurement Systems 2.7 Classifying Components of Uncertainty 2.8 Measurement Errors and Measurement Uncertainties 2.8.1 Random errors 2.8.2 Systemic errors 2.8.3 Tool-to-tool variations 2.9 Uncertainties and Risks 2.10 Are These Traditional Metrics Enough? References 3 Fundamental Metrology: Redefining Measurement System Analysis 3.1 Introduction 3.2 A Metrologist�s Core Activities 3.3 Roadmap and Specifications 3.4 Standards 3.5 Monitor Samples and Process Stressed Artifacts (PSAs) 3.6 Test Vehicle Variability, Metrology-Induced Sample Damage, and Sample Stability 3.7 Reference Measurement System 3.8 Precision 3.8.1 Precision example 3.9 Calculating Precision in the Presence of Measurement-Induced Damage or Sample Changes over Time 3.10 Mandel Regression 3.11 Accuracy 3.11.1 Accuracy example 3.12 TMU: An Alternative Definition for Clarification 3.12.1 Mandel analysis: the building block for new matching terms 3.13 Matching 3.13.1 Matching example 1 3.13.2 Matching example 2 3.14 Sustaining/Stability/Statistical Process Control (SPC) 3.14.1 Using TMP and FMP methodology to calculate SPC control-chart limits 3.14.2 Mean control-chart-limit calculations for each tool 3.14.3 Mean control-chart-limit calculations for the fleet 3.14.4 Control-chart-limit setup example 1 3.14.5 Control-chart-limit setup example 2 3.14.6 Leveraging FMP to determine the root cause to allow the fleet to meet the requirements 3.15 Sampling Plan: Catch-All Major Variations 3.16 Random Sampling 3.17 Systematic Sampling 3.18 Summary References 4 Metrology in the Semiconductor IC Industry 4.1 Pervasiveness of Metrology 4.2 Metrology�s Impact on Time to Market 4.3 Value of Metrology 4.4 Metrology Target Design: an Element of Overhead 4.5 Chip Scaling and an Introduction to Some Key Metrology Toolsets 4.6 Vision System and Recipes 4.7 Toolset Recipe Portability Monitoring 4.8 Large Fleet Sizes: Fleet Management 4.9 IC Process Development and Control 4.10 Metrology in IC Manufacturing Process Control References 5 Metrology Toolsets in IC Manufacturing: Optical Metrology 5.1 Optical Film Characterization: Thickness and Composition 5.2 Scatterometry (OCD) 5.3 Overlay References 6 Metrology Toolsets in IC Manufacturing: Charged-Particle Metrology Systems 6.1 Electron-based Systems 6.2 CD-SEM and Sample Interactions 6.3 Key Fundamental Challenges of the CD-SEM 6.4 SEM-based Overlay Measurements References 7 Metrology Toolsets in IC Manufacturing: Additional Metrology Systems 7.1 X-Ray Metrology 7.2 In situ and Integrated Metrology 7.3 Critical-Dimension Atomic Force Microscope (CD-AFM) References 8 Limitations of Metrology Techniques and Hybrid Metrology 8.1 Introduction 8.2 Hybrid Metrology: Synergies of Multiple Techniques 8.3 Types of HM Implementation References 9 Metrology in Mask Making 9.1 Mask CD Measurements 9.2 Mask Inspection References 10 Perspectives on Future Challenges and Considerations 10.1 Measurement Tooling Challenges 10.2 Fault Detection and Control 10.3 Virtual Metrology 10.4 Waferless Recipe Writing 10.5 The Blurry Line between Metrology and Defect Inspection 10.6 Line-Edge Roughness and 3D Metrology 10.7 Contour Metrology 10.8 Lab-to-Fab and New Technology Trends References We contemplated writing a book about IC manufacturing metrology for years. Each of us in parallel recognized a gap that existed in the field of metrology and inspection. Until now, metrology (not to be confused with meteorology) had no book from the perspective of an engineer in a manufacturing and development environment in the modern IC industry. The closest we could find was a chapter called "Metrology Methods in Photolithography," written by Laurie J. Lauchlan, Diana Nyyssonen from IBM Microelectronics, and Neal Sullivan from DEC, within a book titled Handbook of Microlithography, Micromachining, and Microfabrication, Vol. 1 (SPIE Press, 1997). The other significant text comes from Alain Diebold, in a book titled Handbook of Silicon Semiconductor Metrology (CRC Press, 2001). Numerous other books, especially statistical books, briefly mention metrology in the context of gauge studies, precision-to-tolerance ratios (also called the gauge maker's rule), and repeatability and reproducibility. The three of us combined have been working in semiconductor IC fabs for more than two decades, specializing in metrology in semiconductor manufacturing. This book allows us to share our learning, understanding, and experiences with our fellow engineers and managers. As in other disciplines, metrology is constantly improving, enhancing, and developing to meet ever-increasing needs in today�s high-technology manufacturing. In IC fabs, people refer to metrology equipment as process equipment tools or a fleet of tools. We will use that term in this book to mean metrology equipment or systems. Photomasks, masks, and reticles are all used to describe the photomasks used in IC manufacturing, interchangeably. Many acronyms in IC fabs are used in this book; please refer to the List of Acronyms for their exact meanings. The contents of the book are organized not only for metrology engineers but also for other process engineers and fabmanagers to better understand metrology data and the uncertainties associated with those data. It also serves as a textbook for students and researchers who are interested in metrology in general or as a reference book on fundamentals and latest developments in the IC industry. The first two chapters introduce metrology at its most basic level. The first half of Chapter 1 defines metrology, its origin, and its purpose regardless of the field of practice. The second half of the chapter discusses measurement methods and the measurement process and includes descriptions of operator, machine, and what is being measured along with the evolution of manual and automated measurements. It closes with a discussion on applications of industrial metrology. Chapter 2 explores metrology fundamentals as they pertain to traditional measurement system characterization and calibration. The word "traditional" is used because this is an area where much has changed since the 1997. Chapter 3 discusses the need to improve upon the traditional forms of measurement system characterization and calibration. Many newer concepts are introduced here in the areas of system matching, long-term stability monitoring, and accuracy. Chapter 4 focuses on a particular industrial application of metrology--the semiconductor industry--that has the tightest metrology requirements in the world. It explores areas such as the pervasiveness and value of metrology, target design, and process control. Chapter 5 features optical metrology measurement techniques such as ellipsometry and scatterometry. Chapter 6 presents charged-particle measurement techniques, with a primary focus on scanning electron beam metrology. Chapter 7 explores other measurement techniques not used inline in 1997, such as x-ray and in-situ metrology. Chapter 8 discusses the limits of metrology and the evolution of hybrid metrology. Hybrid metrology development and implementation is another major change. Chapter 9 discusses metrology in mask making, emphasizing the differences as compared to wafer metrology. The final chapter closes with trends, perspectives on future metrology challenges, and other considerations not covered in the other chapters. Example Excel spreadsheets are provided in the accompanying CD in the area of measurement uncertainty analysis--specifically, precision, matching and relative accuracy. These files complement the textbook material and help readers understand the metrology concepts better (as well as leverage these spreadsheets in their own work, as needed). Although there is a significant focus on the semiconductor industry, many of the concepts can be easily applied to other industrial fields. The metrology field has grown significantly over time, especially in the areas of semiconductor manufacturing. With this growth comes an increasing need for metrology expertise. This book is intended to introduce a new generation to metrology while also helping current practitioners. Almost every other major semiconductor discipline, such as lithography and etch, is taught in academia; there is very little metrology material taught currently, and we hope this book helps spark increased academic interest. Bo Su
Pages: 184
ISBN: 9781628418118
Volume: TT101Preface
Eric Solecky
Alok Vaid
August 2015
![]()
1、本站所有分享材料(数据、资料)均为网友上传,如有侵犯您的任何权利,请您第一时间通过微信(lib99net)、QQ(24661067)、电话(17898078618)联系本站,本站将在24小时内回复您的诉求!谢谢!
2、本站所有商品,除特殊说明外,均为(电子版)Ebook,请购买分享内容前请务必注意。特殊商品有说明实物的,按照说明为准。
![]()
![]()
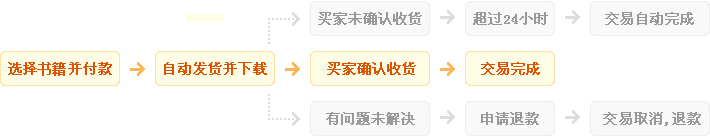
1、自动:在上方保障服务中标有自动发货的宝贝,拍下后,将会自动收到来自卖家的宝贝获取(下载)链接;
2、手动:未标有自动发货的的宝贝,拍下后,卖家会收到邮件、短信提醒,也可通过QQ或订单中的电话联系对方。
![]()
1、描述:书籍描述(含标题)与实际不一致的(例:描述PDF,实际为epub、缺页少页、版本不符等);
2、链接:部分图书会给出链接,直接链接到官网或者其他站点,以便于提示,如与给出不符等;
3、发货:手动发货书籍,在卖家未发货前,已申请退款的;
4、其他:如质量方面的硬性常规问题等。
注:经核实符合上述任一,均支持退款,但卖家予以积极解决问题则除外。交易中的商品,卖家无法对描述进行修改!
![]()
1、在未购买下前,双方在QQ上所商定的内容,亦可成为纠纷评判依据(商定与描述冲突时,商定为准);
2、在宝贝同时有网站演示与图片演示,且站演与图演不一致时,默认按图演作为纠纷评判依据(特别声明或有商定除外);
3、在没有"无任何正当退款依据"的前提下,写有"一旦售出,概不支持退款"等类似的声明,视为无效声明;
4、虽然交易产生纠纷的几率很小,但请尽量保留如聊天记录这样的重要信息,以防产生纠纷时便于网站工作人员介入快速处理。


 人工在线查找书籍,不要问我们有什么,告诉我们您需要什么即可...¥1.00
人工在线查找书籍,不要问我们有什么,告诉我们您需要什么即可...¥1.00 【PPT】Linear Algebra and Its Applica...¥0.1
【PPT】Linear Algebra and Its Applica...¥0.1 Delay-Adaptive Linear Control by Ya...¥29.99
Delay-Adaptive Linear Control by Ya...¥29.99 Handbook of Organic Materials for E...¥19.99
Handbook of Organic Materials for E...¥19.99 FinFET Devices for VLSI Circuits an...¥29.99
FinFET Devices for VLSI Circuits an...¥29.99 Positron Beams and Their Applications¥29.99
Positron Beams and Their Applications¥29.99 ASM Handbook Volume 11A Analysis an...¥420.00
ASM Handbook Volume 11A Analysis an...¥420.00 PETSc for Partial Differential Equa...¥29.99
PETSc for Partial Differential Equa...¥29.99 无机非金属材料热工设备-作 者 : 姜洪舟主编 2015第5版...¥14.99
无机非金属材料热工设备-作 者 : 姜洪舟主编 2015第5版...¥14.99 Product and Process Design Principl...¥9.99
Product and Process Design Principl...¥9.99